A Diac is two terminal , three layer bi directional device which can be switched from its off state for either polarity of applied voltage.

Construction:
The diac can be constructed in either npn or pnp form.The two leads are connected to p-regions of silicon separated by an n region. the structure of diac is similar to that of a transistor differences are
There is no terminal attached to the base layer
The three regions are nearly identical in size. the doping concentrations are identical to give the device symmetrical properties.
When a positive or negative voltage is applied across the terminals of Diac only a small leakage current Ibo will flow through the device as the applied voltage is increased , the leakage current will continue to flow until the voltage reaches breakover voltage Vbo at this point avalanche breakdown of the reverse biased junction occurs and the device exhibits negative resistance i.e current through the device increases with the decreasing values of applied voltage the voltage across the device then drops to breakback voltage Vw
V- I CHARECTERISTICS OF A DIAC
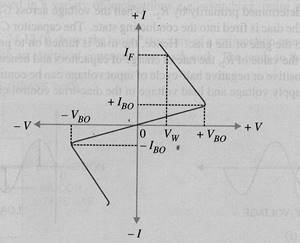
For applied positive voltage less than + Vbo and Negative voltage less than -Vbo , a small leakage current flows thrugh the device. Under such conditions the diac blocks flow of current and behaves as an open circuit. the voltage +Vbo and -Vbo are the breakdown voltages and usually have range of 30 to 50 volts.
When the positive or negative applied voltage is equal to or greater than tha breakdown voltage Diac begins to conduct and voltage drop across it becomes a few volts conduction then continues until the device current drops below its holding current breakover voltage and holding current values are identical for the forward and reverse regions of operation.
Diacs are used for triggering of triacs in adjustable phase control of a c mains power. Applications are light dimming heat control universal motor speed control
Source: http://www.srmuniv.ac.in/downloads/diac.doc
Web site to visit: http://www.srmuniv.ac.in
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes