I C (Internal combustion) Engines
1 Introduction:
Any engine in which, a fuel air mixture is burnt externally or internally , so that the hot gaseous products of the combustion act directly on the surfaces of the of its moving parts such as piston, cylinder etc .We will know about the role of engines on our daily life in detail. Those who are working in the city, they need to travel at least 10-15km min. The mode of transport may be 2 wheeler, 4 wheeler etc.
Many farmers are using a diesel engines for pumping a water from well, canals directly to their farms. Diesel engines are used to run pump set, floor mills, agricultural equipments, generators etc. They are very useful in the areas, where electricity is not reliable. Diesel engine is device which converts chemical energy in the fuel into mechanical energy.
2 Objective:
After the completion of this lesson you will be able to
3. IC Engines ( The Internal Combustion Engine )
 An internal combustion engine is any engine that operates by burning its fuel inside the engine. It converts chemical energy into useful mechanical energy by burning fuel. Chemical energy is released when the fuel-air mixture is ignited by the spark in the combustion chamber. The gas produced in this reaction rapidly expands forcing the piston down the cylinder on the power stroke.
An internal combustion engine is any engine that operates by burning its fuel inside the engine. It converts chemical energy into useful mechanical energy by burning fuel. Chemical energy is released when the fuel-air mixture is ignited by the spark in the combustion chamber. The gas produced in this reaction rapidly expands forcing the piston down the cylinder on the power stroke.
Chemical energy ----burning -- heat -- Pressure --- Speed
In external combustion engines fuel is burnt outside the engine. For e.g in steam engine, fuel is burned in a boiler and then steam is carried out to the engine. A steam is used to obtain rotary motion of the shaft.
In petrol engine and diesel engines, fuel is burnt inside the engine. Engines used in car, motorcycles, diesel engine etc are examples of Internal combustion engine (I.C Engine )
4 Types of Engines

Types of I.C Engines (ctd)
I.C engines are mainly of two types
i. Two stroke engine – two wheeler – mopeds
ii. Four stroke engine – four wheeler – cars, bikes, diesel engine etc.
We will discuss the working of these engines in the following section.
12.1 Intext questions
Fill in the blanks
Following are parts of 2 stroke engine.

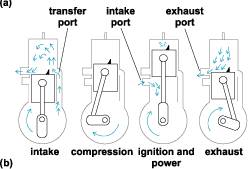
5 Two - Stoke engine
In 2 stoke engine, there are special holes cut on the cylinder wall. These allow air-fuel mixture to enter and exhaust smoke to go out of the engine. These inlet and outlet port, open or closes with the piston.
To understand the operation of 2 stoke engine, we will start with the ignition stoke.
Ignition and power stroke: Piston moves towards spark plug end. Air-fuel mixture gets pressurized in the cylinder. This creates vacuum in the chamber. Intake port gets uncovered and air-fuel mixture is sucked from carburetor. Spark plug ignites air-fuel mixture and explodes. This gives power to piston. Piston starts moving down.
Exhaust stroke:
As piston moves downwards, exhaust ports gets open. Exhaust gases starts exiting the cylinder. Inlet port gets closed and Air-fuel mixture in the chamber starts getting compressed.
Intake Stroke:
Now Air-fuel mixture enters into the cylinder forcing any remaining exhaust gas to go out of the cylinder.
Compression stroke :
Inlet port and outlet port is closed. Piston moves upwards compressing air-fuel mixture in the cylinder.
In the 2 stroke engine, sparks fires once every revolution. Piston going upward or downwards is called a stoke. Since there are 2 stroke in one revolution, the engine is called 2 – stroke engine.
To lubricate crankshaft, connecting rod and cylinder walls, special oil is mixed with petrol. If you do not mix oil in the petrol, the engine isn’t going to last long.
6 Four Stroke Engine ( petrol engine)
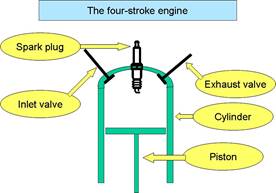
The four-stroke internal combustion engine is most commonly used for automotive and industrial purposes. In four stroke engine, fuel is burnt once in 2 revolutions. Each revolution has 2 strokes and hence it is called 4 stroke engine.
 The four-stroke cycle is more efficient than the two-stroke cycle, but requires considerably more moving parts and manufacturing expertise. Following are the main parts of four stroke engine.
The four-stroke cycle is more efficient than the two-stroke cycle, but requires considerably more moving parts and manufacturing expertise. Following are the main parts of four stroke engine.
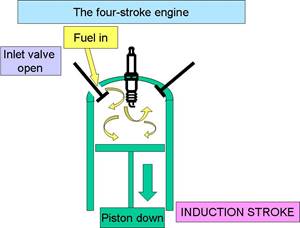
a) Intake stroke –
The cycle begins when piston is at top. Piston moves down, reducing pressure inside. Fuel entered into the cylinder.
b)  Both inlet and outlet valves are closed and pistons moves towards top. Air-fuel mixture gets compressed.
Both inlet and outlet valves are closed and pistons moves towards top. Air-fuel mixture gets compressed.
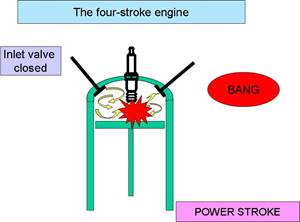
c) Power stroke :
Air-fuel mixture gets ignited at the end of the compression stroke. It gets ignited either by spark plug or by heat and pressure of compression.
The burning fuel exerts pressure on piston, pushing him downwards.
d) Exhaust Stroke
 During this stroke, exhaust valves opens leaving exhaust gases out of the cylinder.
During this stroke, exhaust valves opens leaving exhaust gases out of the cylinder.
Unlike 2 – stroke engine where oil is mixed with the fuel. In 4 – stroke engine, oil is put separately in the crank case. It gets splashed with the movement of crank and does lubrication.
Intext questions 12.2
Fill in the blanks:
7 Basic Parts of diesel Engine :
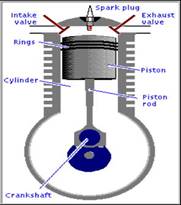
The most essential parts of 4 stroke diesel engine are listed below :-
The engine block is fitted with a cylindrical shaft. This is the cylinder which is hollow and stationary.
The Piston is free to slide up and down within the cylinder.
Combustion Chamber
The fuel mixture is brought into the cylinder then the piston moves up and compresses the fuel into a small space called the combustion chamber. When the fuel is ignited and burns, tremendous pressure builds up. This pressure forces the piston back down the cylinder. The basic motion within the engine is that of the piston sliding up and down the cylinder a reciprocating motion.
It converts reciprocating motion into more useful rotary motion.
These are the doors for admitting fuel mixture and releasing exhaust.
There are two valves, one to let the exhaust out (Exhaust valve) and one to allow the fuel mixture to come in (intake valve).
It is a body of Engine.
It contains most of moving parts of engine.
Piston rings provide a tight seal between the piston and cylinder wall.
The piston rings reduce friction and control the lubrication of cylinder wall.
Three or four piston rings are mounted on a piston.
First two are compression rings. They can move slightly up and down and expand slightly in and out.It act as a power seal ensuring that a maximum amount of the combustion pressure is used in forcing the piston down the cylinder.
The flywheel is mounted on the tapered end of crankshaft.
It helps to smooth out the operation of engine.
12.3 IN TEXT QUESTIONS :-
Fill in the Blanks :
8 OPERATION OF FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE :-
Four stroke cycle means that it take four stroke of the piston to complete the operating cycle of the diesel engine.
Strokes |
Movement of Piston |
Intake Valve |
Exhaust Valve |
Action in combustion chamber/ cylinder |
1. Intake stroke |
Piston moves down |
Open |
Closed |
Fuel and air enters in combustion chamber. |
2. Compression stroke |
Piston moves up |
Closed |
Closed |
A fuel mix is compressed into a small space at the top of cylinder |
3.Power Stroke |
Piston Pushed down |
Closed |
Closed |
Fuel mixture is ignited. It produces a rotary motion in flywheel. |
4. Exhaust stroke |
Piston moves up |
Closed |
Open |
Piston pushes exhaust gases out of cylinder. |
Fig. : Operation of four stroke diesel engine.
In most of the diesel engine, crank is rotated manually till engines fires. During intake stroke, fuel enters into cylinder. It gets compressed while piston moves upwards in return stroke. This is called as compression stroke. Exhaust and inlet valves remains closed while piston return. The temperature of fuel inside the chamber increases with pressure and it bursts, giving thrust to the piston. This is called as power stroke. While piston returns to its initial position, exhaust valves opens and burnt gases are passed out.
Operation of opening and closing of valves is done using Cam fitted on the shaft.
These four strokes complete the engines cycle, means four strokes needs two revolutions of the crankshaft. As soon as one cycle complete, the other begins. If an engine is operating at a speed of 3600 RPM, There are 1800 cycles per minute. Stroke means a regular up & down movement of piston in cylinder.
Fill in the blanks :
1…………….2………………3……………4………………
12.9 Trouble shouting of diesel Engine.
Cause / Fault |
Remedy To Remove it. |
1. No fuel in tank |
Fill tank with fresh fuel. |
2. Water in fuel |
Drain the tank.Clean carburetor and fuel liens. |
3. Improper Carburetor |
Adjust Carburetor. |
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1 |
Carbon in combustion chamber |
Remove the cylinder. |
2. |
Loose flywheel |
Check fly key |
3. |
Loose connecting Rod |
Replace connecting rod. |
Engine Overheats |
||
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1. |
Engine improperly times |
Time the Engine |
2. |
Carburetor improperly adjusted |
Adjusted Carburetor |
3. |
Excessive load on engine |
Check operation of associated equipment |
4. |
Lack of Lubrication |
Full crankcase with proper oil. |
Engine Vibration(heavy) |
||
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1. |
Engine not securely mounted |
Tighten the loose mounting bolts. |
2. |
Bent crankshaft |
Replace crankshaft |
3. |
Associated equipment out of balance |
Check associated equipments |
12.5 IN TEXT QUESTIONS :
Write the sentences are true or false
12.10 What have you learnt ?
12.11 Terminal questions :-
ANSWERS TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 12.1:
Fill in the blanks
ANSWERS TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 12.2:
Fill I the blanks
ANSWERS TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 12.3 :
a) Compression ring & Oil control ring.
b) Cylinder, Piston, Flywheel, Crankshaft, Camshaft piston rings, valves, connecting rod etc.
c) Convert the reciprocating motion into more useful rotary motion.
d) Connecting rod.
e) Reciprocatory
ANSWERS TO IN TEXT QUESTIONS 12.5
True or False
Topic : Diesel Engine
12.1 Introduction :
Many farmers are using a diesel engines for pumping a water from well, canals directly to their farms. Diesel engines are used to run pumpset, floor mills, agricultural equipments, generators etc. They are very useful in the areas, where electricity is not reliable. Diesel engine is device which converts chemical energy in the fuel into mechanical energy.
12.2 Objectives :
After completing this unit the student will be able to
12.3 Diesel Engine :
Basic Parts of diesel Engine :-

The most essential parts of 4 stroke diesel engine are listed below :-
The engine block is fitted with a cylindrical shaft. This is the cylinder which is hollow and stationary.
The Piston is free to slide up and down within the cylinder.
Combustion Chamber
The fuel mixture is brought into the cylinder then the piston moves up and compresses the fuel into a small space called the combustion chamber. When the fuel is ignited and burns, tremendous pressure builds up. This pressure forces the piston back down the cylinder. The basic motion within the engine is that of the piston sliding up and down the cylinder a reciprocating motion.
It converts reciprocating motion into more useful rotary motion.
These are the doors for admitting fuel mixture and releasing exhaust.
There are two valves, one to let the exhaust out (Exhaust valve) and one to allow the fuel mixture to come in (intake valve).
It is a body of Engine.
It contains most of moving parts of engine.
Piston rings provide a tight seal between the piston and cylinder wall.
The piston rings reduce friction and control the lubrication of cylinder wall.
Three or four piston rings are mounted on a piston.
First two are compression rings. They can move slightly up and down and expand slightly in and out.
It act as a power seal ensuring that a maximum amount of the combustion pressure is used in forcing the piston down the cylinder.
The flywheel is mounted on the tapered end of crankshaft.
It help to smooth out the operation of engine.
Fig. 3.1 Basic parts of four cycle engine.
Fill in the Blanks :
12.5 OPERATION OF FOUR STROKE DIESEL ENGINE :-
Four stroke cycle means that it take four stroke of the piston to complete the operating cycle of the diesel engine.
Strokes |
Movement of Piston |
Intake Valve |
Exhaust Valve |
Action in combustion chamber/ cylinder |
1. Intake stoke |
Piston moves down |
Open |
Closed |
Fuel and air enters in combustion chamber. |
2. Compression stroke |
Piston moves up |
Closed |
Closed |
A fuel mix is compressed into a small space at the top of cylinder |
3.Power Stroke |
Piston Pushed down |
Closed |
Closed |
Fuel mixture is ignited. It produces a rotary motion in flywheel. |
4. Exhaust stroke |
Piston moves up |
Closed |
Open |
Piston pushes exhaust gases out of cylinder. |
Fig. : Operation of four stroke diesel engine.
In most of the diesel engine, crank is rotated manually till engines fires. During intake stroke, fuel enters into cylinder. It gets compressed while piston moves upwards in return stroke. This is called as compression stroke. Exhaust and inlet valves remains closed while piston return. The temperature of fuel insider the chamber increases with pressure and it bursts, giving thrust to the piston. This is called as power stroke. While piston returns to its initial position, exhaust valves opens and burned gases are passed out.
Operation of opening and closing of valves is done using Cam fitted on the shaft.
These four strokes complete the engines cycle, means four strokes needs two revolutions of the crankshaft. As soon as one cycle complete, the another begins. If an engine is operating at a speed of 3600 RPM. These are 1800 cycles per minute.
Stroke means a regular up & down movement of piston in cylinder.
Fill in the blanks :
12.6 Trouble shouting of diesel Engine.
* Engine starts with difficulty *
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1. No fuel in tank |
Fill tank with fresh fuel. |
2. Water in fuel |
Drain the tank. |
3. Improper Carburetor |
Adjust Carburetor. |
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1 |
Carbon in combust on chamber |
Remove the cylinder. |
2. |
Loose flywheel |
Check fly key |
3. |
Loose connecting Rod |
Replace connecting rod. |
Engine Overheats |
||
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1. |
Engineer improperly times |
Time the Engine |
2. |
Carburetor improperly adjusted |
Adjusted Carburetor |
3. |
Excessive load on engine |
Check operation of associated equipment |
4. |
Lack of Lubrication |
Full crankcase with proper oil. |
Engine Vibrater excessively. |
||
|
Cause / Fault |
Remedy / To Remove it. |
1. |
Engine not securely mounted |
Tighten loose mounting bolts. |
2. |
Bent crankshaft |
Replace crankshaft |
3. |
Associated equipment out of balance |
Check associated equipments |
12.3 IN TEXT QUESTIONS :
Write the sentences are true or false
12.7 What have you learnt ?
In this lesson you have learn ,
12.8 Terminal questions :-
ANSWERS TO INTEXT QUESTIONS 12.1 :
a) Types of piston rings (1) Compression ring
(2) Oil control ring.
Cylinder, Piston, Flywheel, Crankshaft, Camshaft piston rings, valves, connecting rod etc.
c) Crankshaft is used to convert the reciprocating motion into more useful rotary motion.
12.3 ANSWERS TO IN TEXT QUESTIONS :-
True or False
Source: http://learningwhiledoing.in/UploadedFiles/LessonFile/Energy_Electrical_Electrical%20Services_Document_Diesel%20Engine.doc
http://learningwhiledoing.in/UploadedFiles/LessonFile/Energy_Electrical_Electrical%20Services_Document_IC%20Engine.doc
Web site to visit: http://learningwhiledoing.in
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes