Fasteners in Aviation
(Slide 3)
Temporary Fastening
(Slide 4)
Temporary Fastening
(Slide 5)
Threaded Fasteners
(Slide 6)
Threaded Fasteners
(Slide 7)

(Slide 8)
Thread Terminology

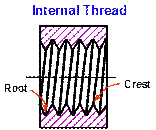
(Slide 9)
Thread Terminology

(Slide 10)
Thread Terminology
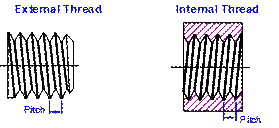
(Slide 11)
Types of Thread Form

(Slide 12)
Thread Standard

(Slide 13)
Thread Drawings
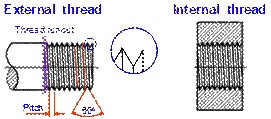
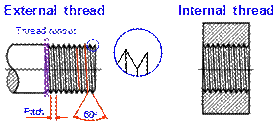
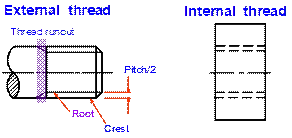
(Slide 14)
Bolt Terminology
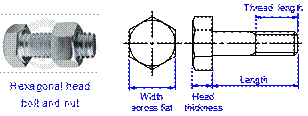
(Slide 15)
Bolt Application
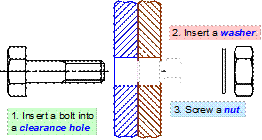
(Slide 16)
Bolt Application - Engine
(Slide 17)
Screw Terminology
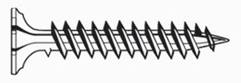
(Slide 18)
Screw Application


(Slide 19)
Screws Application - Fuselage
(Slide 20)
Screws Application - Engine
Source: http://www.elcamino.edu/academics/indtech/nsf/docs/intro_to_fastener_technology_instructor_notes_part3_R2010.doc
Web site to visit: http://www.elcamino.edu
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes