It is a common practice which is to be carried out in two main stages.
I Preliminary Investigation The purposes of preliminary investigations are to provide sufficient information to find out the practicability of the proposed scheme and to choose between alternative schemes. The preliminary designs and estimations can be prepared and recommendations are made with reasonable confidence.
2. Final investigations The final investigation include the detailed exploration of the recommended site so as to establish the complete suitability and to enable the final designs. The preliminary and final investigations include mainly (a) hydrological (b) topographical and (c) geological
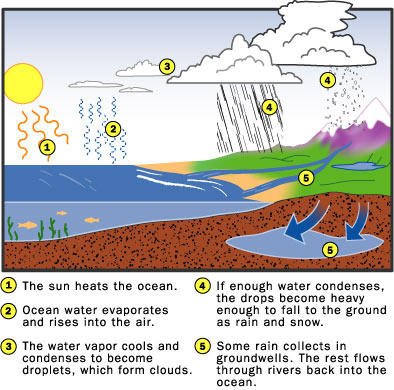
Hydrologic Cycle
Air-current cycles drive the Earth's water supply through a cycle of its own, called the hydrologic cycle. As the sun heats liquid water, the water evaporates into vapor in the air. The sun heats the air, causing the air to rise in the atmosphere. The air is colder higher up, so as the water vapor rises, it cools, condensing into droplets. When enough droplets accumulate in one area, the droplets may become heavy enough to fall back to Earth as precipitation.
Principle
Hydroelectric power generated by converting the hydraulic potential energy from water into electrical energy.
Layout of Hydroelectric Power Plants
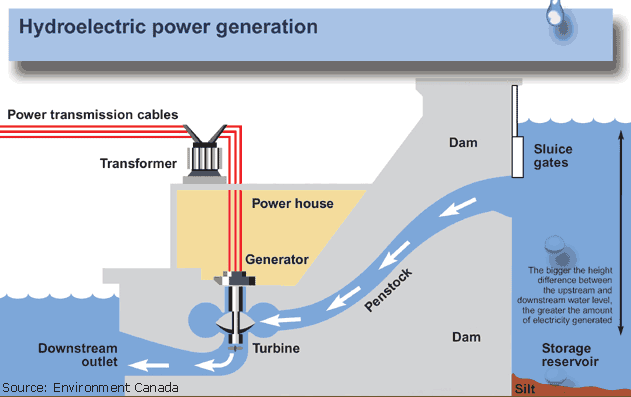
Hydroelectric power plants are suitable were water with suitable head are available. The layout shows the important parts of hydroelectric plant. The different parts of a hydroelectric power plant are
(1) Dam
Dams are structures built over rivers to stop the water flow and form a reservoir. The reservoir stores the water flowing down the river. This water is diverted to turbines in power stations. The dams collect water during the rainy season and stores it, thus allowing for a steady flow through the turbines throughout the year. Dams are also used for controlling floods and irrigation. The dams should be water-tight and should be able to withstand the pressure exerted by the water on it. There are different types of dams such as arch dams, gravity dams and buttress dams. The height of water in the dam is called head race.
(2) Spillway
A spillway as the name suggests could be called as a way for spilling of water from dams. It is used to provide for the release of flood water from a dam. It is used to prevent over toping of the dams which could result in damage or failure of dams. Spillways could be controlled type or uncontrolled type. The uncontrolled types start releasing water upon water rising above a particular level. But in case of the controlled type, regulation of flow is possible.
(3) Penstock and Tunnel
Penstocks are pipes which carry water from the reservoir to the turbines inside power station. They are usually made of steel and are equipped with gate systems. Water under high pressure flows through the penstock. A tunnel serves the same purpose as a penstock. It is used when an obstruction is present between the dam and power station such as a mountain.
(4) Surge Tank
Surge tanks are tanks connected to the water conductor system. It serves the purpose of reducing water hammering in pipes which can cause damage to pipes. The sudden surges of water in penstock is taken by the surge tank, and when the water requirements increase, it supplies the collected water thereby regulating water flow and pressure inside the penstock.
(5) Power Station
Power station contains a turbine coupled to a generator. The water brought to the power station rotates the vanes of the turbine producing torque and rotation of turbine shaft. This rotational torque is transferred to the generator and is converted into electricity. The used water is released through the tail race. The difference between head race and tail race is called gross head and by subtracting the frictional losses we get the net head
URL: http://ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/hyhowworks.html
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydroelectricity
Question Bank:
PART – A
PART – B
1. With neat sktch explain the construction and working principle of hydor electric power plant.
Source: http://www.srmuniv.ac.in/downloads/hydro.doc
Web site to visit: http://www.srmuniv.ac.in
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes