Karnaugh map
A Karnaugh map is a diagram consisting of a small number of non-overlapping (mutually exclusive) rectangles used to indicate the relationship between elements of a set and given properties or attributes. When two properties or attributes are involved, the corresponding Karnaugh map is also called a two-way table.
Suppose a set of attribute blocks has several shapes (squares, circles, triangles and hexagons) of various colours (red, blue, yellow), size (small, large) and thickness (thin, thick). If we consider the properties red (colour) and square (shape), then any of the blocks from the set will satisfy exactly one of the following four combinations of these two properties: it is red and square; it is red and not square; it is not red and square; it is not red and not square. This can be represented diagrammatically using a Karnaugh map, where each attribute block is place in exactly one of the four regions as shown below:
Note that the properties of size and thickness are not represented in this diagram. Each of the shapes shown could be small or large, thick or thin. If, for example, a third property such as thickness (thin, thick) were to be considered then previous Karnaugh map could be modified to have eight regions as follows:
Kite
A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides equal.

A kite may be convex (as shown in the diagram above left) or non-convex (as shown above right). The axis of each kite is shown.
See also: adjacent, axis, polygon, reflection.
L
Line
A line is a basic or undefined geometric object that is taken as a given. Intuitively lines model what is perceived visually as straight. Lines have one dimension and extend indefinitely in the plane. They have the relation to points that any two distinct points lie on a unique line, which is said to pass through and contain the two points. A ruler or straight edge is used to draw part of a line.
See also: line segment, undefined term.
Line segment
If A and B are two points on a line, the part of the line between and including A and B is called a line segment or interval. The distance AB is a measure of the size or length of AB.

Any point A on a line divides the line into two pieces called rays. The ray AP is that ray which contains the point P (and the point A). The point A is called the vertex of the ray and it lies on the ray.
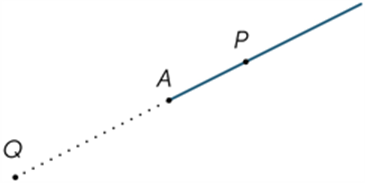
See also: line, ray.
Linear equation
A linear equation is an equation involving just linear terms, that is, polynomials of degree 1. The general form of a linear equation in one variable is ![]() , for example
, for example
![]() See also: equation, variable.
See also: equation, variable.
Location
A description of position with respect to some fixed reference.
Location (statistics)
A measure of location is a single number that can be used to indicate a central or ‘typical value’ within a set of data. The most commonly used measures of location are the mean and the median although the mode is also sometimes used for this purpose.
Logarithm
The logarithm of a positive number ![]() is the power to which a given number
is the power to which a given number ![]() , called the base, must be raised in order to produce the number
, called the base, must be raised in order to produce the number ![]() . The logarithm of
. The logarithm of ![]() , to the base
, to the base ![]() is denoted by
is denoted by ![]() . Algebraically:
. Algebraically: ![]() .
.
For example, ![]() because
because ![]() , and
, and ![]() because
because ![]() .
.
Logic
Principles of reasoning where one proposition is deduced from other propositions according to the given rules of inference.
Lowest common multiple (lcm)
Given any two natural numbers, their lowest common multiple is the smallest natural number which they both divide exactly. This is not necessarily their product. For example, the lcm of 6 and 9 is 18, since 3 × 6 = 18 and 2 × 9 = 18, but 6 × 9 = 54. The lcm of two numbers may be found by listing the multiples of both numbers and finding the first common multiple. For example, the first four multiples of 6 are: 6, 12, 18 and 24, while the first four multiples of 9 are: 9, 18, 27 and 36. The first (lowest) multiple in common is 18.
The lcm is used, for example, in the operation of addition and subtraction of fractions and to identify equivalent fractions with the same denominator. See also: natural number.
M
Magnitude
The size, or absolute value of a number; for example, both +5 and -5 have magnitude 5. The magnitude of certain numbers can only be approximated to a given accuracy, for example the magnitude of the number π, correct to two decimal places, is 3.14.
Many-to-one correspondence
See: correspondence.
Mass
The mass of an object measures how much matter the object contains. The SI unit for mass is the kilogram (kg). Mass does not change with a change in gravitational acceleration, as weight does. An object will have the same mass on Earth as on the moon where the gravitational acceleration is much less. See also: weight.
Mean
Also called the average. The sum of values in a data set divided by the total number of values in the data set. For example, if a data set consists of the values ![]() then the mean
then the mean ![]() is defined as:
is defined as:
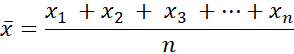
For example, for the following list of five numbers { 2, 3, 3, 6, 8 } the mean equals ![]() .
.
See also: median.
Measure
A measure is a record of the magnitude of an attribute (such as weight, length, time, and likelihood) associated with an object or event. See also: magnitude.
Measure of centre (central tendency)
This is a statistic that is used to represent a data set. There are three common measure of centre for a data set: mode (the most common value), median (the middle value) and the mean (the sum of all the values divided by the number of values).
See: mean, median, mode.
Median
The median is the value in a set of ordered data that divides the data into two equal parts. It is frequently called the ‘middle value’. Where the number of observations is odd, the median is simply the middle value. For an even set of elements, the mode is taken to be the average of the two middle values. For example, the median of the numbers 1, 3, 4, 5, 7 is 4, while the median for 1, 3, 4, 5 is the average of the two middle values, that is
(3 + 4) ÷ 2 = 3.5.
The median provides a measure of location of a data set that is suitable for both symmetric and skewed distributions and is also less sensitive to outliers than the mean.
See also: mean, outliers, skew.
Mensuration formulas
Mensuration formulas define the measure of one quantity as a function of other quantities using an algebraic formula. For example, the area, ![]() , of a circle radius,
, of a circle radius, ![]() , is defined by the mensuration formula
, is defined by the mensuration formula ![]() and the average speed,
and the average speed, ![]() , of a moving object which travels a distance
, of a moving object which travels a distance ![]() in time
in time ![]() is defined by the formula
is defined by the formula ![]() .
.
For selected specific formulae, see: volume, area.
Midpoint
The midpoint M of a line segment (interval) AB is the point that divides the segment into two equal parts.
Let A(x1, y1) be points in the Cartesian plane. Then the midpoint M of line segment AB has coordinates ![]() . This can be seen from the congruent triangles below.
. This can be seen from the congruent triangles below.

Mode
The mode is the most frequently occurring value in a set of data. There can be more than one mode. When there are two modes, the data set is said to be bimodal. The mode is sometimes used as a measure of location.
See also: bimodal, multimodal.
Modelling
Modelling is using mathematical concepts, structures and relationships to describe and characterise, or model, a situation in a way that captures its essential features.
Multimodal data
Data with a distribution that has more than one mode.
See: mode.
Multiple
A multiple of a number is the product of that number and an integer. A multiple of a real number ![]() is any number that is a product of
is any number that is a product of ![]() and an integer. For example,
and an integer. For example, ![]() and -10.5 are multiples of
and -10.5 are multiples of ![]() because
because ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Multiplication
For positive natural numbers, the multiplication of ![]() and
and ![]() may be considered adding a number
may be considered adding a number ![]() to itself
to itself ![]() times, or the number
times, or the number ![]() to itself
to itself ![]() times (since multiplication is a commutative operation).
times (since multiplication is a commutative operation).
The multiplicative operator in algebra is the symbol ![]() , called the multiplication sign. The multiplication
, called the multiplication sign. The multiplication ![]() may also be represented
may also be represented ![]() or
or ![]() . The result of the multiplication
. The result of the multiplication ![]() is called the product, while the numbers
is called the product, while the numbers ![]() and
and ![]() are factors of this product. Multiplication is also both an associative and distributive operation.
are factors of this product. Multiplication is also both an associative and distributive operation.
Multiplication can also be defined in other mathematical contexts, for example with matrices, but the precise definition for the action of the multiplication operator will vary.
See also: associative, distributive, commutative, multiples, multiplicative situations.
Multiplicative situations
Multiplicative situations are problems or contexts that involve multiplication (or division). Calculating the number of seats in a theatre that has 30 rows of 24 seats, finding equivalent fractions, and working with ratios and percentages, are all multiplicative situations.
N
Natural number
A natural number is an element of the infinite set of numbers N = {0, 1, 2, 3 ...}. Natural numbers are sometimes also referred to as counting numbers. An even natural number is an element of the set {0, 2, 4, 6 ...}. An odd natural number is an element of the set {1, 3, 5, 7 ...}.
In some references, the number 0 is not included in the set of natural numbers; however, it is useful to include 0 to correspond to the number of elements in an empty set, or a count of none.
See also: number, even number, odd number.
Negative number
A real number ![]() is a negative number if
is a negative number if ![]() . The set of negative integers
. The set of negative integers![]()
![]() , and is sometimes referred to as ‘the negative counting numbers’.
, and is sometimes referred to as ‘the negative counting numbers’.
Negative numbers may be rational or irrational. For example, the number ![]() is a negative real number that is also a rational number. The solutions of the equation
is a negative real number that is also a rational number. The solutions of the equation
![]() are
are ![]() and
and ![]() . The solution
. The solution![]() is a negative real number that is also irrational.
is a negative real number that is also irrational.
See also: irrational number, rational number.
Net
A net is a plane figure that can be folded to form a polyhedron. More specifically, it is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional object, comprising joined shapes that can be folded to form the object.
There are nets for polyhedra, cylinders and cones, and net for approximations of a sphere. One possible net for a cube is shown below:

Network
A set of points (vertices or nodes) some of which are joined by lines or curves (edges) which sometimes enclose regions (faces) is a network. Networks are used to represent relationships involving connectedness; for example, road networks, a family tree or the edges lining a tennis court. See also: vertex.
Node
A vertex in a network. See also: network.
Non-negative integers
Also called the positive integers, an element of the infinite set of numbers ![]() = {1, 2, 3 ...}.
= {1, 2, 3 ...}.
See also: integer.
Normal distribution
The distribution for a random variable which has a characteristic bell-shaped curve. Variables such as height and IQ typically have a Normal type distribution.
See also: variable, distribution
Number
See: integer, rational number, irrational number, natural number.
Number Line
A number line gives a pictorial representation of real numbers. Part of a number line showing the integers is given below:
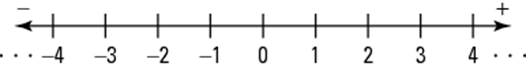
Number sentence
A number sentence is an equation or inequality, using common symbols and operations. A number sentence may be used to represent a situation. For example, the total number of pets I own if I have three cats and one dog could be shown using 3 + 1 = 4.
See also: inequality, equation, operation.
Numeral
The designation of a number in a given language; for example, the number ‘three’ is designated by the Hindu-Arabic numeral 3, the Roman numeral III, and the Chinese numeral 三.
Numerator
The numerator is the term ![]() in a fraction
in a fraction ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are integers and
are integers and ![]() . For example, the numerator of
. For example, the numerator of ![]() is
is ![]() . If an object is divided into
. If an object is divided into ![]() equal parts, then the fraction
equal parts, then the fraction ![]() represents
represents ![]() of these parts taken together. For example, if a line segment is divided into
of these parts taken together. For example, if a line segment is divided into ![]() equal parts, each of those parts is one fifth of the whole and 3 of these parts taken together corresponds to the fraction
equal parts, each of those parts is one fifth of the whole and 3 of these parts taken together corresponds to the fraction ![]() . See also: fraction.
. See also: fraction.
Numerical data
Numerical data is data associated with a numerical variable. See: numerical variable
Numerical variable
Numerical variables are variables whose values are numbers, and for which arithmetic processes such as adding and subtracting, or calculating an average, make sense.
A discrete numerical variable is a numerical variable, each of whose possible values is separated from the next by a definite ‘gap’. Common numerical variables often have the numbers {0, 1, 2, 3…} as possible values. Other examples could include prices measured in dollars and cents, the number of children in a family or the number of days in a month.
See also: numerical data
O
Observed frequency
See: frequency.
Obtuse angle
See: angle.
Odd number
An odd number is an integer that is not divisible by 2. The odd numbers are
![]() . See also: natural number.
. See also: natural number.
One-to-one correspondence
See: correspondence.
Operation
The process of combining numbers or expressions. In the primary years, operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. In later years, operations include substitution and composition.
Opposite angle
See: vertically opposite angle.
Order
Order is a relation that describes the location of elements in a set with respect to each other. These elements may be totally ordered or partially ordered.
For example, the set of natural numbers is totally ordered by the relation ‘less than or equal to’ since, for any two natural numbers ![]() and
and ![]() , exactly one of the following is true:
, exactly one of the following is true:
![]() ,
, ![]() or
or ![]() . Similarly, the set of students in a class can be totally ordered with respect to their height using the relation ‘less than or equal to’.
. Similarly, the set of students in a class can be totally ordered with respect to their height using the relation ‘less than or equal to’.
However, the set of people at a school fair is only partially ordered by the relation ‘is a parent of’ since there will likely be many pairs of people who are not each other’s parent, such as siblings.
Order of operations
A set of conventions for evaluating arithmetic expressions that involve several operations. In general brackets (parentheses) can be used to provide priority, otherwise the order of operations from left to right is exponents (powers, indices), then multiplication/division then addition/subtraction. For example, in 5 – 6 ÷ 2 + 7, the division is performed first and the expression becomes 5 – 3 + 7 = 9. If the convention is ignored and the operations are performed in order, a different result of 6.5 is obtained.
See also: addition, division, index, multiplication, subtraction.
Source: https://victoriancurriculum.vcaa.vic.edu.au/LearningArea/LoadFile?learningArea=mathematics&subject=mathematics&name=Mathematics%20Glossary.docx&storage=Glossary
Web site to visit:ttps://victoriancurriculum.vcaa.vic.edu.au
Author of the text: indicated on the source document of the above text
If you are the author of the text above and you not agree to share your knowledge for teaching, research, scholarship (for fair use as indicated in the United States copyrigh low) please send us an e-mail and we will remove your text quickly. Fair use is a limitation and exception to the exclusive right granted by copyright law to the author of a creative work. In United States copyright law, fair use is a doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without acquiring permission from the rights holders. Examples of fair use include commentary, search engines, criticism, news reporting, research, teaching, library archiving and scholarship. It provides for the legal, unlicensed citation or incorporation of copyrighted material in another author's work under a four-factor balancing test. (source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fair_use)
The information of medicine and health contained in the site are of a general nature and purpose which is purely informative and for this reason may not replace in any case, the council of a doctor or a qualified entity legally to the profession.
The texts are the property of their respective authors and we thank them for giving us the opportunity to share for free to students, teachers and users of the Web their texts will used only for illustrative educational and scientific purposes only.
All the information in our site are given for nonprofit educational purposes